In the US alone, fraud losses increased 14% between 2022 and 2023 - and they are increasing globally. The financial industry is particularly vulnerable to fraud, and also bears a unique responsibility to combat it, both to protect customers and to remain compliant.
Fraud transaction monitoring is a key piece of any robust anti-fraud program. By automatically monitoring transactions to flag suspicious behavior, financial institutions effectively take a proactive approach to preventing and detecting fraudulent behavior. This article explores the role transaction monitoring plays in anti-fraud activities and how advanced analytics technology can help improve on traditional systems that turn up too many false positives and false negatives.
Fraud transaction monitoring, or simply fraud monitoring, involves continuously screening all transactions related to customer accounts and payment activities for patterns and behaviors that may indicate fraudulent activity. This includes monitoring debit and credit card transactions and wire transfers. It may also monitor other activities such as changes to account information like adding new beneficiaries, adjustments to personal identification details, and even device login activity across digital banking channels. It is a key component of modern anti-fraud systems.
The goal of fraud transaction monitoring systems is to identify potentially fraudulent transactions in as close to real-time as possible, before they can be fully processed and funds successfully stolen. Sophisticated monitoring solutions analyze a broad range of data points and employ advanced analytics, machine learning models, and rules engines to accurately distinguish legitimate transactions from likely instances of fraud.
Anti-fraud transaction monitoring is critical for financial institutions and payment processors because it enables the fast identification of suspicious patterns of behavior across customer accounts and transactions. By automatically analyzing transaction data in real-time or near real-time, monitoring systems can signal potentially fraudulent activities the moment they occur.
The ability to detect suspicious transactions quickly is vital, letting organizations take immediate action to investigate the flagged activities and halt any confirmed cases of fraud before significant financial damage can take place. This protects not only the bank or payment processor itself, but also safeguards their customers from the consequences of fraud.
Beyond mitigating active fraud incidents, transaction monitoring also plays an important preventative role. The patterns and behaviors that get flagged provide valuable insights that can be fed back into an organization's fraud prevention frameworks. This information can be used to enhance fraud detection models, update risk scoring rules, and inform employee training programs focused on identifying emerging fraud tactics.
Beyond the clear benefits of transaction monitoring for fraud detection and prevention, it also plays an important role in keeping organizations like banks and payment services compliant with regulatory requirements. As an example, in Europe, payment service providers are required to comply with the Payment Services Directive (PSD2). This regulation establishes transaction monitoring as a requirement: all but the lowest risk transactions must be monitored constantly.
Fraud transaction monitoring systems rely on multiple types of technology, including alerting systems, risk scoring engines, and machine learning and AI. The typical layers within a transaction monitoring system are:
- Data collection
- Creating detection rules
- Alerting
- Investigating and reporting
Traditional monitoring systems come with certain drawbacks for fraud analysts. Static alerting rules may fail to capture the full context around suspicious activity leading to false negatives. Or, they may cast too wide a net resulting in false positives that dominate investigators’ time and lead to poor customer experiences.
And when it comes to investigating alerts, tools based on tabular data can make it time-consuming to investigate incidents, as it’s difficult to see the connections between entities.
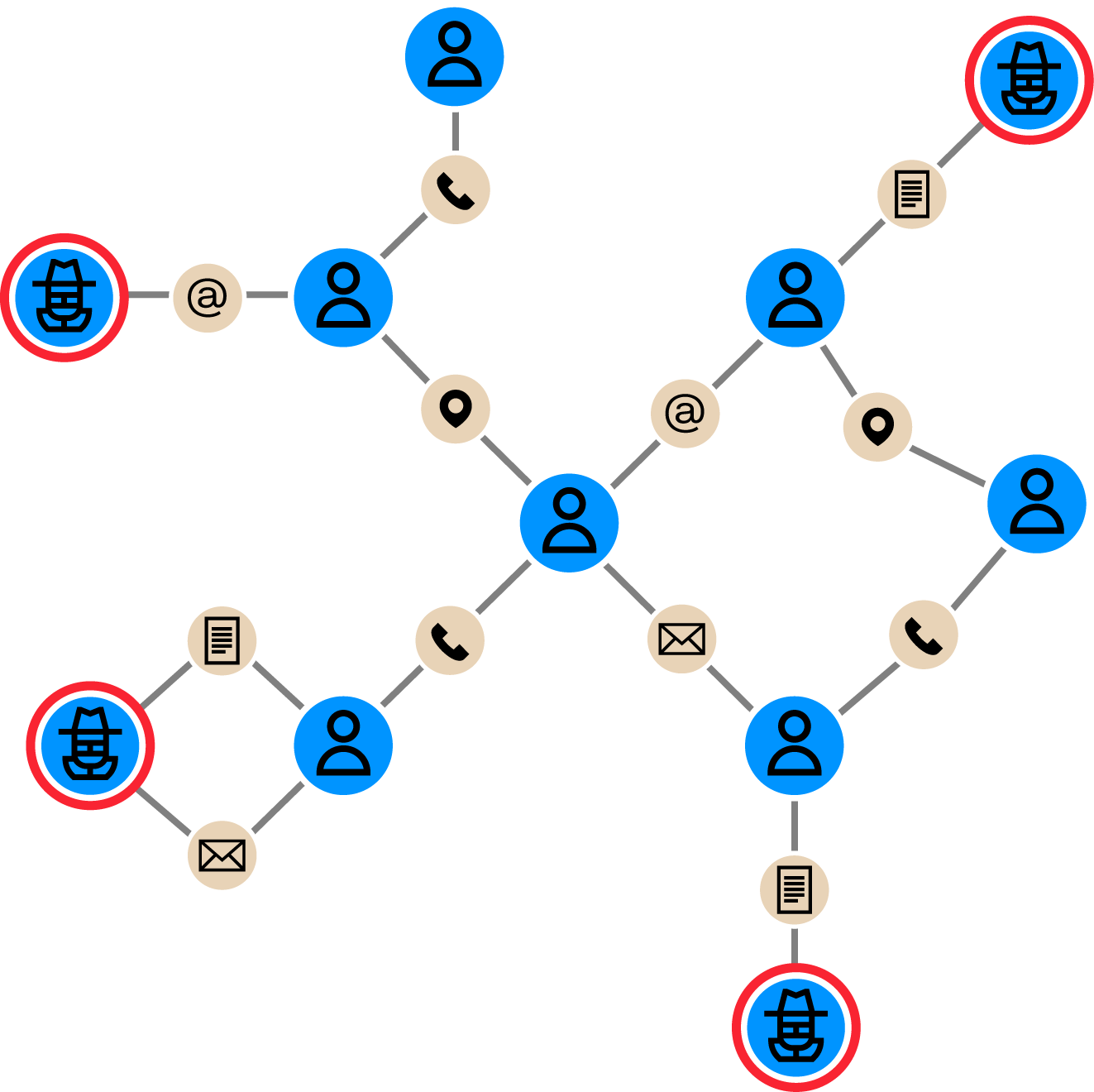
Graph is a way of storing and modeling data that allows users to query, visualize and explore relationships between data points scattered across a wide range of data sources. That can include both internal data (like KYC data) and third-party data sources.
Graph is an ideal solution for alerting and investigating within a fraud transaction monitoring system. It provides a natural way of modeling relationships, making it far easier to understand the connections between entities that may indicate suspicious behavior.
Graph analytics and visualization offer benefits for transaction monitoring and help solve for some of the challenges of traditional tools.
- Graph visualization - displaying data as an interconnected web - facilitates the understanding of contextual information and patterns of interest, saving time on information retrieval and analysis.
- Graph solutions can seamlessly integrate with other tools in your transaction monitoring stack. This lets you leverage graph analytics and graph embeddings to deliver additional input to machine learning models.
- Graph technology is well suited for de-siloing data. In a context like fraud transaction monitoring that requires analysis of multiple data sources, often both internal and external, graph provides a 360 degree view of clients and their direct and indirect connections to enhance transaction monitoring.
With software like the graph visualization and analytics solutions from Linkurious, your organization can go beyond simple, static rules to build context into alerts. Linkurious helps eliminate blindspots in transaction monitoring for more accurate and speedy detection and investigation.

